5G in autonomous vehicles is paving the way for a new era of transportation, where cutting-edge technology meets the open road. From enhancing safety to improving efficiency, the integration of 5G is set to redefine the driving experience as we know it. Get ready to dive into the world of autonomous vehicles powered by 5G technology.
In this article, we will explore the crucial role of 5G in revolutionizing autonomous vehicles, from enabling real-time data transmission to enhancing decision-making processes. Let’s buckle up and take a ride into the future of transportation.
Overview of 5G in Autonomous Vehicles
G technology plays a crucial role in enhancing the capabilities of autonomous vehicles by providing faster and more reliable connectivity. With the ability to transmit data in real-time, 5G networks enable autonomous vehicles to make split-second decisions based on up-to-the-moment information, ultimately improving their overall performance and safety on the road.
Real-Time Data Transmission
- 5G networks facilitate real-time data transmission between autonomous vehicles and the surrounding environment, including other vehicles, infrastructure, and pedestrians.
- This instantaneous communication allows autonomous vehicles to react quickly to changing road conditions, potential hazards, and unexpected obstacles.
- By receiving and processing real-time data, autonomous vehicles can optimize their routes, adjust speeds, and navigate complex traffic scenarios more efficiently.
Benefits of 5G Integration
- Improved Safety: The fast and reliable connectivity offered by 5G technology enhances the safety of autonomous vehicles by reducing the risk of accidents and collisions.
- Enhanced Efficiency: With real-time data transmission capabilities, autonomous vehicles can operate more efficiently, leading to smoother traffic flow and reduced congestion on the roads.
- Enhanced User Experience: Integrating 5G with autonomous vehicles can provide passengers with a more comfortable and convenient ride, as the vehicles can navigate routes and traffic conditions with precision and agility.
5G Infrastructure for Autonomous Vehicles: 5G In Autonomous Vehicles
Implementing 5G in autonomous vehicles requires a robust infrastructure to support the high-speed, low-latency communication needs of self-driving cars.
Infrastructure Requirements for 5G in Autonomous Vehicles
For successful integration of 5G in autonomous vehicles, the infrastructure must include:
- High-density small cell networks to ensure seamless connectivity
- Low-latency edge computing capabilities for real-time data processing
- Advanced cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive vehicle data
- Reliable and high-bandwidth backhaul connections for efficient data transmission
Comparison of Infrastructure Challenges
Existing networks face challenges such as:
- Limited bandwidth leading to congestion and delays
- Higher latency affecting real-time communication
- Potential security vulnerabilities due to outdated protocols
5G infrastructure overcomes these challenges with its high-speed, low-latency, and secure communication capabilities.
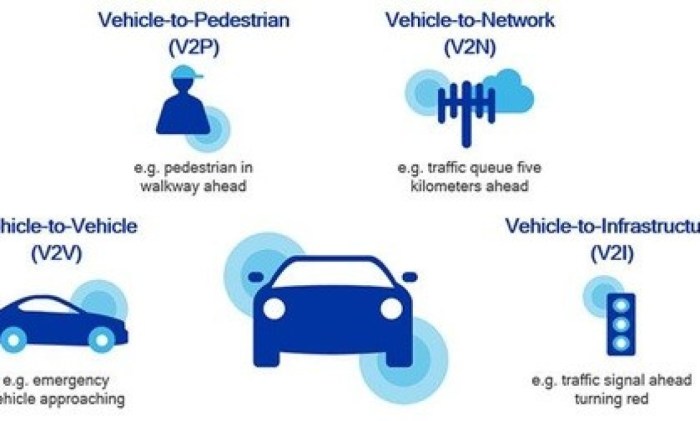
Support for V2X Communication
5G infrastructure plays a crucial role in enabling V2X communication in autonomous vehicles by:
- Facilitating vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication for coordinated driving
- Enabling vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication for traffic management
- Supporting vehicle-to-pedestrian (V2P) communication for enhanced safety
Data Processing and Edge Computing
In the realm of autonomous vehicles, data processing and edge computing play crucial roles in ensuring real-time decision-making and enhancing overall performance.
5G Enables Faster Data Processing and Reduced Latency
- 5G technology provides significantly higher data speeds and lower latency compared to previous generations, allowing autonomous vehicles to process vast amounts of data quickly.
- With 5G, autonomous vehicles can communicate with other vehicles, infrastructure, and cloud servers in real-time, enabling faster decision-making and response times on the road.
- The reduced latency in 5G networks ensures that critical data, such as sensor information and navigation updates, are processed swiftly to enhance the safety and efficiency of autonomous driving.
Role of Edge Computing in Conjunction with 5G Networks
- Edge computing brings data processing closer to the source of data generation, reducing the need to send all information to centralized cloud servers.
- By leveraging edge computing in conjunction with 5G networks, autonomous vehicles can process data locally, enabling faster decision-making and reducing dependency on distant data centers.
- This distributed computing approach enhances the overall speed and reliability of data processing, critical for the seamless operation of autonomous vehicles in dynamic environments.
Examples of Edge Computing Enhancing Decision-Making in Autonomous Vehicles
- Edge computing allows autonomous vehicles to analyze sensor data in real-time at the edge of the network, enabling immediate responses to changing road conditions without delays.
- By processing data locally, edge computing enables autonomous vehicles to make split-second decisions, such as collision avoidance or lane changes, without relying solely on cloud-based processing.
- In scenarios where network connectivity is limited or disrupted, edge computing ensures that autonomous vehicles can continue to operate efficiently and safely by processing essential data locally.
Security and Privacy Considerations
When it comes to integrating 5G technology into autonomous vehicles, there are several security risks that need to be addressed to ensure the safety and privacy of the data being transmitted and processed.
Security Risks
- Remote Hacking: With the increased connectivity of 5G networks, there is a risk of malicious actors gaining unauthorized access to the vehicle’s systems, potentially leading to accidents or data breach.
- Data Interception: As data is transmitted wirelessly over 5G networks, there is a possibility of interception by cybercriminals, compromising sensitive information.
- Denial of Service Attacks: Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on continuous data exchange for navigation and decision-making. Any interruption in this data flow due to a denial of service attack can pose serious safety risks.
Data Security and Privacy Measures, 5G in autonomous vehicles
- End-to-End Encryption: Data transmitted between the vehicle and the network is encrypted to prevent unauthorized access or tampering.
- Secure Authentication Protocols: Strong authentication methods are implemented to ensure that only authorized entities can access the vehicle’s systems and data.
- Data Minimization: Only necessary data is collected and stored to reduce the risk of exposure in case of a security breach.
Encryption and Authentication Protocols
- Encryption: Data is encrypted using advanced algorithms to protect it from being intercepted or altered during transmission.
- Authentication: Two-factor authentication and biometric authentication methods are used to verify the identity of users and ensure secure access to the vehicle’s systems.
- Secure Communication Channels: Secure communication protocols such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) are employed to establish a secure connection between the vehicle and the network.
